

Alkaline earth metal reactivity trend full#
The outer shell will more easily attract another electron, which needs an electron to complete its full outer shell, when there is more attractive force.Ī useful mnemonic picture to help you recall that:Īs you go up group 7 (the halogens), again the elements get more reactive. Groups in the Periodic Table of Elements Click on an element to read about the chemical and physical properties of the group to which that element belongs. The fewer electron shells (rings) between the nucleus and the outer shell (ring) also has less shielding effect and again this increases the electron attraction. Youll find more specific groups, like transition metals, rare earths, alkali metals, alkaline earth, halogens, and noble gasses. All the alkaline earth metals are highly reactive elements since they have a strong tendency to lose the two valence s-electrons to form the corresponding. The distance "a" is less than "c" and the force of attraction between the nucleus and the outer shell increases with shorter distances. For example, all alkaline earth metals are silvery-white.
The elements of this group are quite similar in their physical and chemical properties. alkaline earth metals Atomic radius increases down the group MgBa Reactivity of with water (and solubility of metal hydroxides) increases down the group. This group of elements includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium.
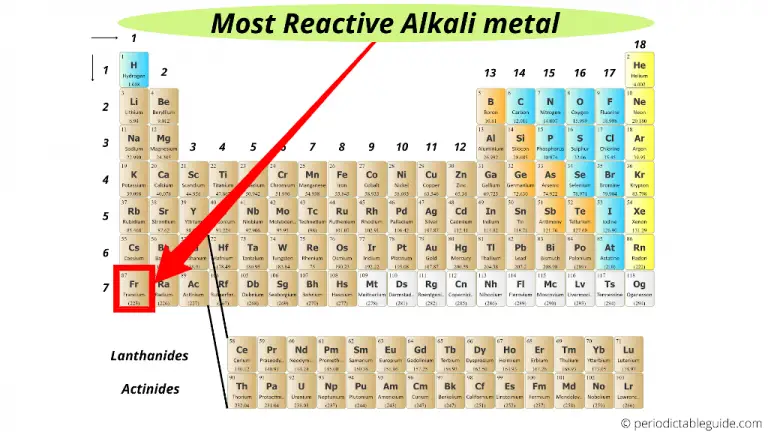
Halogens from bromide to fluorine get more reactive because the force of attraction between the nucleus (core) and the outer electron get stronger as you go up group 7 elements. The alkaline earth metals are the elements that correspond to group 2 of the modern periodic table. The largest atomic radius of elements in their period. Why do halogens get more reactive going upwards in group 7? The alkaline-earth metals- beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium- are a reactive group of metals. Highly reactive, with reactivity increasing moving down the group. The reaction between magnesium and water is usually slow because magnesium readily reacts. The outer electron is more easily transferred to say an oxygen atom, which needs electrons to complete its full outer shell. Trends in Reactivity of Group 2 Elements (alkaline-earth metals). The more electron shells (rings) between the nucleus and outer electron also creates shielding and again this weakens the nuclear attraction. The distance "c" is greater than "a" and the force of attraction between the nucleus and the outer shell (rings) diminishes with distance. Why do alkali metals get more reactive going down group 1?Īlkali metals from lithium to potassium get more reactive because the force of attraction between the nucleus (core) and the outer electron gets weaker as you go down group 1 elements. As you go down group 1 (the alkali metals) in the periodic table, the elements get more reactive.Īs you go up group 7 (the halogens), again, the elements become more reactive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
